1808 United States Presidential Election on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The 1808 United States presidential election was the sixth quadrennial
File:James Madison.jpg, Secretary of State
from
from
George Clinton
from
File:George Clinton by Ezra Ames.jpg, Vice President
George Clinton
from
from
from
from
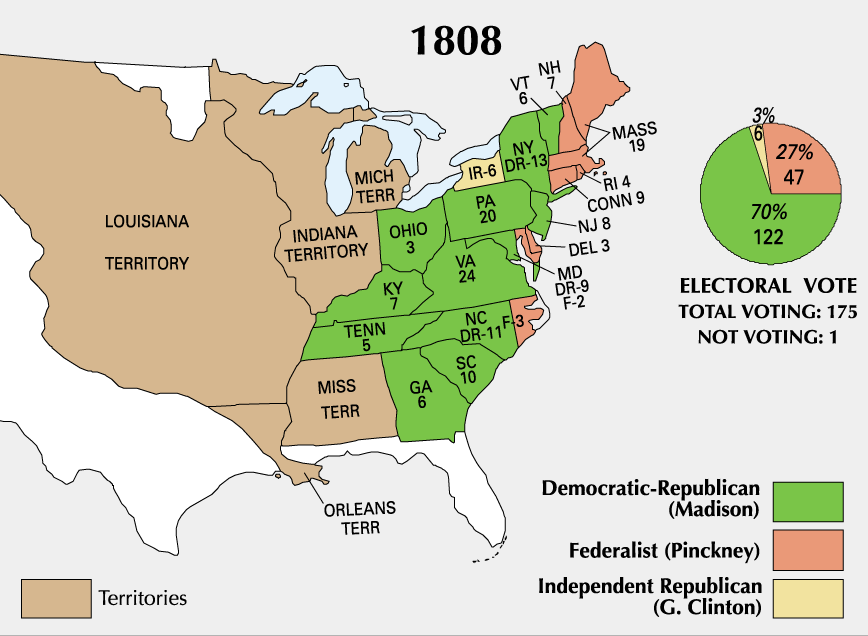 Pinckney retained the electoral votes of the two states that he carried in 1804 (Connecticut and Delaware), and he also picked up New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and three electoral districts in North Carolina besides the two electoral districts in Maryland that he carried earlier. Except for the North Carolina districts, all of the improvement was in
Pinckney retained the electoral votes of the two states that he carried in 1804 (Connecticut and Delaware), and he also picked up New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and three electoral districts in North Carolina besides the two electoral districts in Maryland that he carried earlier. Except for the North Carolina districts, all of the improvement was in
Source (Popular Vote): ''A New Nation Votes: American Election Returns 1787-1825''
Source (Electoral Vote): (a) ''Only 10 of the 17 states chose electors by popular vote.''
(b) ''Those states that did choose electors by popular vote had widely varying restrictions on suffrage via property requirements.''
(c) ''One Elector from Kentucky did not vote.''
Election of 1808 in Counting the Votes
from the Library of Congress *
A New Nation Votes: American Election Returns, 1787-1825
{{Authority control Presidency of James Madison James Madison
presidential election
A presidential election is the election of any head of state whose official title is President.
Elections by country
Albania
The president of Albania is elected by the Assembly of Albania who are elected by the Albanian public.
Chile
The pre ...
, held from Friday, November 4, to Wednesday, December 7, 1808. The Democratic-Republican
The Democratic-Republican Party, known at the time as the Republican Party and also referred to as the Jeffersonian Republican Party among other names, was an American political party founded by Thomas Jefferson and James Madison in the early ...
candidate James Madison
James Madison Jr. (March 16, 1751June 28, 1836) was an American statesman, diplomat, and Founding Father. He served as the fourth president of the United States from 1809 to 1817. Madison is hailed as the "Father of the Constitution" for hi ...
defeated Federalist
The term ''federalist'' describes several political beliefs around the world. It may also refer to the concept of parties, whose members or supporters called themselves ''Federalists''.
History Europe federation
In Europe, proponents of de ...
candidate Charles Cotesworth Pinckney
Charles Cotesworth Pinckney (February 25, 1746 – August 16, 1825) was an American Founding Father, statesman of South Carolina, Revolutionary War veteran, and delegate to the Constitutional Convention where he signed the United States Constit ...
decisively.
Madison had served as Secretary of State since President
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
*President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966–2010 Japanese ful ...
Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (April 13, 1743 – July 4, 1826) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, architect, philosopher, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the third president of the United States from 18 ...
took office in 1801. Jefferson, who had declined to run for a third term, threw his strong support behind Madison, a fellow Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth ar ...
n. Sitting Vice President
A vice president, also director in British English, is an officer in government or business who is below the president (chief executive officer) in rank. It can also refer to executive vice presidents, signifying that the vice president is on t ...
George Clinton and former Ambassador James Monroe
James Monroe ( ; April 28, 1758July 4, 1831) was an American statesman, lawyer, diplomat, and Founding Father who served as the fifth president of the United States from 1817 to 1825. A member of the Democratic-Republican Party, Monroe was ...
both challenged Madison for leadership of the party, but Madison won his party's nomination and Clinton was re-nominated as vice president. The Federalists chose to re-nominate Pinckney, a former ambassador who had served as the party's 1804
Events
January–March
* January 1 – Haiti gains independence from France, and becomes the first black republic, having the only successful slave revolt ever.
* February 4 – The Sokoto Caliphate is founded in West Africa.
* Februa ...
nominee.
Despite the unpopularity of the Embargo Act of 1807
The Embargo Act of 1807 was a general trade embargo on all foreign nations that was enacted by the United States Congress. As a successor or replacement law for the 1806 Non-importation Act and passed as the Napoleonic Wars continued, it repr ...
, Madison won the vast majority of electoral votes outside of the Federalist stronghold of New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York to the west and by the Canadian provinces ...
. Clinton received six electoral votes for president from his home state of New York. This election was the first of two instances in American history in which a new president was selected but the incumbent vice president won re-election, the other being in 1828.
Nominations
Democratic-Republican Party nomination
Presidential candidates
*James Madison
James Madison Jr. (March 16, 1751June 28, 1836) was an American statesman, diplomat, and Founding Father. He served as the fourth president of the United States from 1809 to 1817. Madison is hailed as the "Father of the Constitution" for hi ...
(Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth ar ...
), Secretary of State
* James Monroe
James Monroe ( ; April 28, 1758July 4, 1831) was an American statesman, lawyer, diplomat, and Founding Father who served as the fifth president of the United States from 1817 to 1825. A member of the Democratic-Republican Party, Monroe was ...
(Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth ar ...
), Former U.S. Ambassador to the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
* George Clinton (New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
), Vice President of the United States
The vice president of the United States (VPOTUS) is the second-highest officer in the executive branch of the U.S. federal government, after the president of the United States, and ranks first in the presidential line of succession. The vice ...
James Madison
James Madison Jr. (March 16, 1751June 28, 1836) was an American statesman, diplomat, and Founding Father. He served as the fourth president of the United States from 1809 to 1817. Madison is hailed as the "Father of the Constitution" for hi ...
from
Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth ar ...
File:James Monroe White House portrait 1819.jpg, Former U.S. Ambassador James Monroe
James Monroe ( ; April 28, 1758July 4, 1831) was an American statesman, lawyer, diplomat, and Founding Father who served as the fifth president of the United States from 1817 to 1825. A member of the Democratic-Republican Party, Monroe was ...
from
Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth ar ...
File:George Clinton by Ezra Ames.jpg, Vice President George Clinton
from
New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
Vice-presidential candidates
* George Clinton (New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
), Vice President of the United States
The vice president of the United States (VPOTUS) is the second-highest officer in the executive branch of the U.S. federal government, after the president of the United States, and ranks first in the presidential line of succession. The vice ...
* John Langdon
John is a common English name and surname:
* John (given name)
* John (surname)
John may also refer to:
New Testament
Works
* Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John
* First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John
* Second ...
(New Hampshire
New Hampshire is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the northeastern United States. It is bordered by Massachusetts to the south, Vermont to the west, Maine and the Gulf of Maine to the east, and the Canadian province of Quebec t ...
), Governor
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, ranking under the head of state and in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of state's official representative. Depending on the type of political ...
* Henry Dearborn
Henry Dearborn (February 23, 1751 – June 6, 1829) was an American military officer and politician. In the Revolutionary War, he served under Benedict Arnold in his expedition to Quebec, of which his journal provides an important record ...
(Massachusetts
Massachusetts (Massachusett language, Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut assachusett writing systems, məhswatʃəwiːsət'' English: , ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is the most populous U.S. state, state in the New England ...
), Secretary of War
The secretary of war was a member of the U.S. president's Cabinet, beginning with George Washington's administration. A similar position, called either "Secretary at War" or "Secretary of War", had been appointed to serve the Congress of the ...
* John Quincy Adams
John Quincy Adams (; July 11, 1767 – February 23, 1848) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, and diarist who served as the sixth president of the United States, from 1825 to 1829. He previously served as the eighth United States S ...
(Massachusetts
Massachusetts (Massachusett language, Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut assachusett writing systems, məhswatʃəwiːsət'' English: , ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is the most populous U.S. state, state in the New England ...
), United States Senator
The United States Senate is the Upper house, upper chamber of the United States Congress, with the United States House of Representatives, House of Representatives being the Lower house, lower chamber. Together they compose the national Bica ...
George Clinton
from
New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
File:John langdon.jpg, Governor John Langdon
John is a common English name and surname:
* John (given name)
* John (surname)
John may also refer to:
New Testament
Works
* Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John
* First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John
* Second ...
from
New Hampshire
New Hampshire is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the northeastern United States. It is bordered by Massachusetts to the south, Vermont to the west, Maine and the Gulf of Maine to the east, and the Canadian province of Quebec t ...
File:Gilbert Stuart - Major-General Henry Dearborn - 1913.793 - Art Institute of Chicago.jpg, Secretary of War Henry Dearborn
Henry Dearborn (February 23, 1751 – June 6, 1829) was an American military officer and politician. In the Revolutionary War, he served under Benedict Arnold in his expedition to Quebec, of which his journal provides an important record ...
from
Massachusetts
Massachusetts (Massachusett language, Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut assachusett writing systems, məhswatʃəwiːsət'' English: , ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is the most populous U.S. state, state in the New England ...
File:Gilbert Stuart - John Quincy Adams - Google Art Project.jpg, Senator John Quincy Adams
John Quincy Adams (; July 11, 1767 – February 23, 1848) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, and diarist who served as the sixth president of the United States, from 1825 to 1829. He previously served as the eighth United States S ...
from
Massachusetts
Massachusetts (Massachusett language, Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut assachusett writing systems, məhswatʃəwiːsət'' English: , ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is the most populous U.S. state, state in the New England ...
Caucus
Senator Stephen R. Bradley, who had chaired thecongressional nominating caucus The congressional nominating caucus is the name for informal meetings in which American congressmen would agree on whom to nominate for the Presidency and Vice Presidency from their political party.
History
The system was introduced after George W ...
during the 1804 presidential election, made a call for the 1808 caucus to the 146 Democratic-Republican
The Democratic-Republican Party, known at the time as the Republican Party and also referred to as the Jeffersonian Republican Party among other names, was an American political party founded by Thomas Jefferson and James Madison in the early ...
members of the United States Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature of the federal government of the United States. It is bicameral, composed of a lower body, the House of Representatives, and an upper body, the Senate. It meets in the U.S. Capitol in Washing ...
and Federalist
The term ''federalist'' describes several political beliefs around the world. It may also refer to the concept of parties, whose members or supporters called themselves ''Federalists''.
History Europe federation
In Europe, proponents of de ...
allies. The caucus was attended by 89 to 94 members of Congress.
The caucus was held in January 1808, and Secretary of State James Madison
James Madison Jr. (March 16, 1751June 28, 1836) was an American statesman, diplomat, and Founding Father. He served as the fourth president of the United States from 1809 to 1817. Madison is hailed as the "Father of the Constitution" for hi ...
won the presidential nomination with the support of President Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (April 13, 1743 – July 4, 1826) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, architect, philosopher, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the third president of the United States from 18 ...
against James Monroe
James Monroe ( ; April 28, 1758July 4, 1831) was an American statesman, lawyer, diplomat, and Founding Father who served as the fifth president of the United States from 1817 to 1825. A member of the Democratic-Republican Party, Monroe was ...
and Vice President George Clinton. The caucus voted to give the vice-presidential nomination to Clinton against his main opponent John Langdon
John is a common English name and surname:
* John (given name)
* John (surname)
John may also refer to:
New Testament
Works
* Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John
* First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John
* Second ...
although Clinton's supporters believed that he would receive the Federalist's presidential nomination, but it instead went to Charles Cotesworth Pinckney
Charles Cotesworth Pinckney (February 25, 1746 – August 16, 1825) was an American Founding Father, statesman of South Carolina, Revolutionary War veteran, and delegate to the Constitutional Convention where he signed the United States Constit ...
. A committee of fifteen members was selected to manage Madison's campaign.
Seventeen Democratic-Republicans in Congress opposed Madison's selection and the caucus system whose authority to select presidential and vice-presidential candidates was disputed. Clinton also opposed the caucus system. Monroe was nominated by a group of Virginia Democratic-Republicans, and although he did not actively try to defeat Madison, he also refused to withdraw from the race. Clinton was also supported by a group of New York Democratic-Republicans for president even as he remained the party's official vice presidential candidate.
Balloting
Federalist Party nomination
The Federalist caucus met in September 1808 and re-nominated the party's 1804 ticket, which consisted of GeneralCharles Cotesworth Pinckney
Charles Cotesworth Pinckney (February 25, 1746 – August 16, 1825) was an American Founding Father, statesman of South Carolina, Revolutionary War veteran, and delegate to the Constitutional Convention where he signed the United States Constit ...
of South Carolina
)''Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no)
, anthem = " Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind"
, Former = Province of South Carolina
, seat = Columbia
, LargestCity = Charleston
, LargestMetro = ...
and former Senator Rufus King
Rufus King (March 24, 1755April 29, 1827) was an American Founding Father, lawyer, politician, and diplomat. He was a delegate for Massachusetts to the Continental Congress and the Philadelphia Convention and was one of the signers of the Unit ...
of New York.
General election
Campaign
The election was marked by opposition to Jefferson'sEmbargo Act of 1807
The Embargo Act of 1807 was a general trade embargo on all foreign nations that was enacted by the United States Congress. As a successor or replacement law for the 1806 Non-importation Act and passed as the Napoleonic Wars continued, it repr ...
, a halt to trade with Europe that disproportionately hurt New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York to the west and by the Canadian provinces ...
merchants and was perceived as favoring France over Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands
* Great Britain, the largest island in the United King ...
. Nonetheless, Jefferson was still very popular with Americans generally and Pinckney was soundly defeated by Madison, though not as badly as in 1804. Pinckney received few electoral votes outside of New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York to the west and by the Canadian provinces ...
.
Results
 Pinckney retained the electoral votes of the two states that he carried in 1804 (Connecticut and Delaware), and he also picked up New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and three electoral districts in North Carolina besides the two electoral districts in Maryland that he carried earlier. Except for the North Carolina districts, all of the improvement was in
Pinckney retained the electoral votes of the two states that he carried in 1804 (Connecticut and Delaware), and he also picked up New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and three electoral districts in North Carolina besides the two electoral districts in Maryland that he carried earlier. Except for the North Carolina districts, all of the improvement was in New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York to the west and by the Canadian provinces ...
.
Monroe won a portion of the popular vote in Virginia and North Carolina, while the New York legislature split its electoral votes between Madison and Clinton.
Source (Popular Vote): ''United States Presidential Elections, 1788-1860: The Official Results by County and State''Source (Popular Vote): ''A New Nation Votes: American Election Returns 1787-1825''
Source (Electoral Vote): (a) ''Only 10 of the 17 states chose electors by popular vote.''
(b) ''Those states that did choose electors by popular vote had widely varying restrictions on suffrage via property requirements.''
(c) ''One Elector from Kentucky did not vote.''
Popular vote by state
The popular vote totals used are the elector from each party with the highest total of votes. The vote totals of North Carolina and Tennessee appear to be incomplete.Close states
States where the margin of victory was under 5%: # New Hampshire, 4.8% (1,292 votes) States where the margin of victory was under 10%: # Rhode Island, 6.6% (380 votes) # North Carolina, 7.55% (1,306 votes)Electoral college selection
See also
*History of the United States (1789–1849)
This article covers the history of the United States from 1789 through 1849, the period of westward expansion.
George Washington was elected the first president in 1789. On his own initiative he created three departments: State (Thomas Jefferso ...
* First inauguration of James Madison
The first inauguration of James Madison as the List of presidents of the United States, fourth president of the United States was held on Saturday, March 4, 1809, in the chamber of the United States House of Representatives, House of Representati ...
* 1808 and 1809 United States House of Representatives elections
* 1808 and 1809 United States Senate elections
References
Further reading
* Brant, Irving, "Election of 1808" in Arthur Meier Schlesinger and Fred L. Israel, eds. ''History of American presidential elections, 1789-1968: Volume 1'' (1971) pp 185-249 * Carson, David A. "Quiddism and the Reluctant Candidacy of James Monroe in the Election of 1808," ''Mid-America'' 1988 70(2): 79–89External links
Election of 1808 in Counting the Votes
from the Library of Congress *
A New Nation Votes: American Election Returns, 1787-1825
{{Authority control Presidency of James Madison James Madison